
A Comprehensive Guide to the Collar Option Strategy
Introduction:
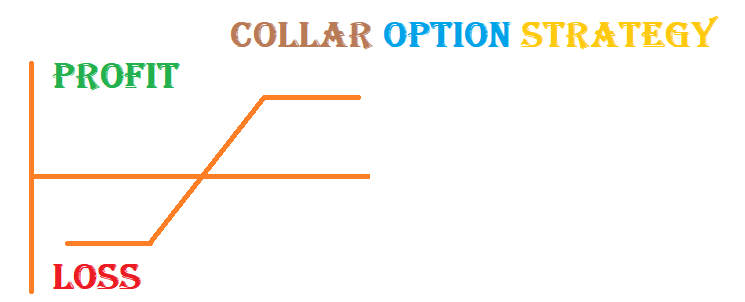
In the options trading, various strategies cater to different risk appetites and market conditions. One such strategy that strikes a balance between risk mitigation and potential for profit is the Collar Option Strategy. The collar strategy is designed to protect the value of an underlying asset while still allowing for some potential upside.
Understanding the Collar Option Strategy:
The collar option strategy involves the simultaneous purchase of a protective put option and the sale of a covered call option against an existing stock or other asset holding. The strategy aims to limit downside risk while potentially generating income from the sale of the call option.
Components of a Collar:
- Long Stock Position:
- The collar strategy starts with owning a particular stock or asset. This underlying position serves as the foundation for implementing the collar strategy.
- Protective Put:
- To protect against potential downside risk, a put option is purchased. This put option acts as insurance, providing the right to sell the underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specific time frame (expiration date). The protective put provides a floor to potential losses if the stock price declines.
- Covered Call:
- Simultaneously with purchasing the put option, a call option is sold against the underlying asset. The call option generates income and potentially offsets the cost of purchasing the put option. The call option obligates the collar strategy holder to sell the underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specific time frame (expiration date).
Key Features and Benefits:
- Downside Risk Mitigation:
- The protective put option serves as an insurance policy, limiting potential losses in case the stock price drops significantly. This feature provides peace of mind for investors concerned about sudden market downturns.
- Income Generation:
- Selling the covered call option generates income, which can help offset the cost of purchasing the put option. The income generated from the call option sale can also act as a buffer against minor downward movements in the stock price.
- Customizable Risk-Reward Profile:
- By adjusting the strike prices of the put and call options, investors can tailor the collar strategy to meet their risk tolerance and profit objectives. This flexibility allows for the optimization of risk management and potential returns.
- Limited Upside Potential:
- The collar strategy's primary trade-off is capping the potential upside gains. Selling the call option restricts the profit potential if the stock price surges beyond the call's strike price.
- Cost of the Protective Put:
- The purchase of a put option incurs a cost, which reduces the overall profitability of the collar strategy. Investors need to assess whether the potential benefits and downside protection justify the expense of the put option.
- Careful Option Selection:
- Choosing the appropriate strike prices and expiration dates for the put and call options is crucial to strike the right balance between risk management and income generation. Thorough analysis and understanding of market conditions are essential for making informed decisions.
- Purchase a protective put:
- You buy a put option with a strike price of $45 and an expiration date three months from now. This put option gives you the right to sell your 100 shares of XYZ Company at $45 per share within the specified time frame.
- Sell a covered call:
- Simultaneously, you sell a call option with a strike price of $55 and the same expiration date. By selling this call option, you are obligating yourself to sell your 100 shares of XYZ Company at $55 per share if the call option is exercised.
- If the stock price of XYZ Company remains between $45 and $55:
- If the stock price of XYZ Company rises above $55:
- The call option you sold may be exercised, and you would have to sell your shares at $55 per share. Although you miss out on any further gains above $55, you still benefit from the initial rise in the stock price.
The protective put option remains unused, as the stock price remains above the put's strike price. - If the stock price of XYZ Company drops below $45:
- The protective put option provides you with downside protection. You can exercise the put option and sell your shares at the higher strike price, mitigating losses.
- The call option you sold remains out-of-the-money and expires worthless. You still keep the premium received from selling the call option.
Considerations and Trade-Offs:
For Example :
Let's say you own 100 shares of XYZ Company, currently trading at $50 per share. You are concerned about a potential market downturn but still want to participate in any upside movement. To implement the collar strategy, you decide to:
Case 1.
The protective put option acts as insurance, protecting you from significant losses if the stock price drops. If the stock price falls below $45, you can exercise the put option and sell your shares at the higher strike price.
The call option you sold remains out-of-the-money and expires worthless. You keep the premium received from selling the call option as income.
Case 2.
Case 3.
By implementing the collar strategy, you have limited the potential downside risk of owning the stock while generating income from the sale of the call option. The strategy allows you to navigate uncertain market conditions and protect your investment, albeit with a capped upside potential.