
Fibonacci Retracement - A Powerful Tool for Technical Analysis
Understanding Fibonacci Retracement
Fibonacci Retracement and Extension Calculator
Introduction
Fibonacci retracement is a popular tool used in technical analysis to identify potential levels of support and resistance. Named after the Italian mathematician Leonardo Fibonacci, this tool is based on the Fibonacci sequence, a series of numbers where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones. In trading, Fibonacci retracement levels are used to predict areas where a financial asset's price might experience a reversal or a significant price move.
What is Fibonacci Retracement?
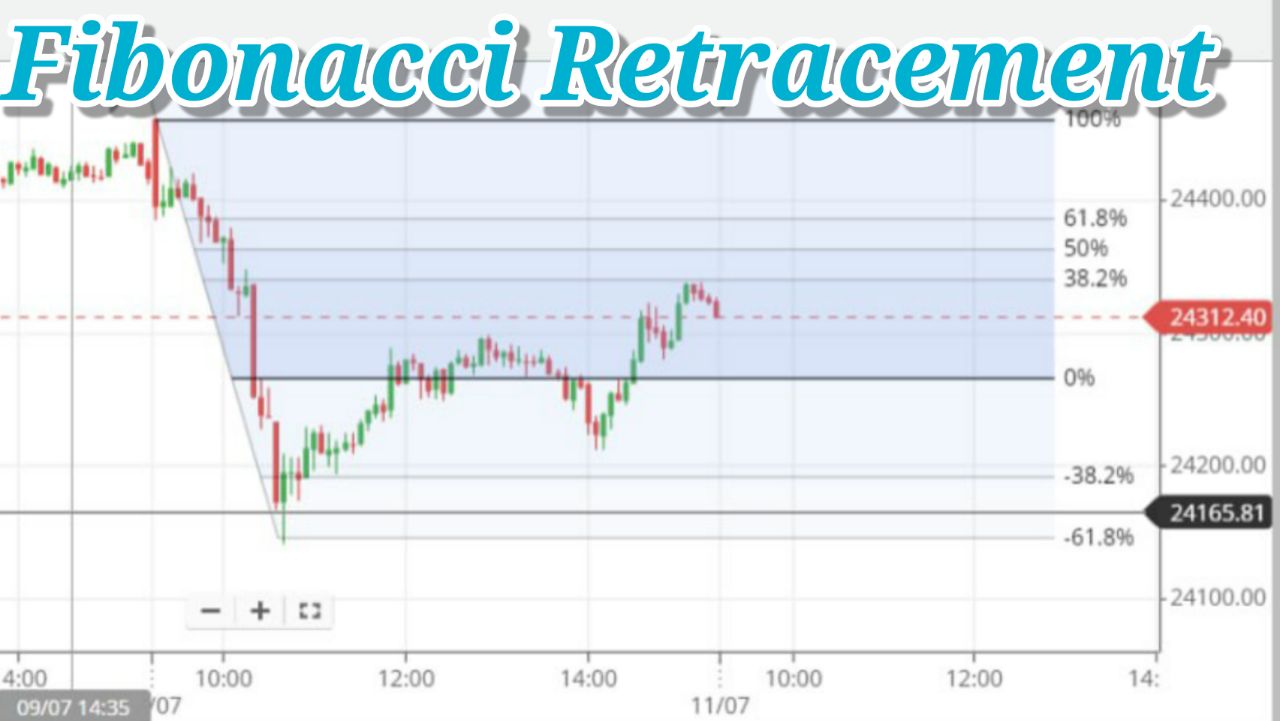
Fibonacci retracement levels are horizontal lines that indicate potential support and resistance levels where price could reverse direction. These levels are derived from the Fibonacci sequence, particularly the key ratios of 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100%. Traders use these levels to identify potential reversal points and make informed trading decisions.
The Fibonacci Sequence
The Fibonacci sequence begins with 0 and 1, and each subsequent number is the sum of the two preceding numbers. The sequence looks like this: 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, and so on. The significance of the Fibonacci sequence in trading lies in the ratios derived from the numbers in the sequence.
The key Fibonacci ratios are derived as follows:
- 23.6%: This is derived by dividing a number in the sequence by the number that is three places to the right.
- 38.2%: This is derived by dividing a number in the sequence by the number that is two places to the right.
- 50%: Although not a true Fibonacci ratio, the 50% level is commonly used as it represents a significant retracement point in price action.
- 61.8%: This is derived by dividing a number in the sequence by the number that immediately follows it.
- 100%: This represents the full retracement of the price movement.
How to Draw Fibonacci Retracement Levels
To draw Fibonacci retracement levels, follow these steps:
- Identify the high and low points of a price movement. In an uptrend, the low point is the starting point, and the high point is the ending point. In a downtrend, the high point is the starting point, and the low point is the ending point.
- Using a Fibonacci retracement tool, draw a line from the starting point to the ending point. The tool will automatically generate the key Fibonacci retracement levels between these two points.
- The resulting horizontal lines represent potential levels of support (in an uptrend) or resistance (in a downtrend) where price may retrace before continuing in the direction of the trend.
Using Fibonacci Retracement in Trading
Fibonacci retracement levels are used by traders to identify potential entry and exit points in the market. Here are some common strategies for using Fibonacci retracement levels:
1. Identifying Potential Reversal Points
Traders use Fibonacci retracement levels to identify areas where price may reverse direction. For example, in an uptrend, if price retraces to the 61.8% level and then starts to move higher, this may be seen as a potential buying opportunity. Similarly, in a downtrend, if price retraces to the 38.2% level and then starts to move lower, this may be seen as a potential selling opportunity.
2. Setting Stop-Loss Orders
Fibonacci retracement levels can also be used to set stop-loss orders. For instance, if a trader enters a long position at the 50% retracement level, they might set a stop-loss order below the 61.8% level to limit potential losses if the trade does not move in their favor.
3. Determining Take-Profit Levels
Traders can use Fibonacci retracement levels to set take-profit orders. For example, if a trader enters a long position at the 38.2% level, they might set a take-profit order at the previous high (100% retracement level) or at another Fibonacci extension level beyond the previous high.
Fibonacci Extensions
In addition to retracement levels, Fibonacci extensions are used to identify potential areas where price may extend beyond the original trend. Fibonacci extension levels include 127.2%, 161.8%, 200%, and 261.8%. These levels can be used to set target prices for trades.
Limitations of Fibonacci Retracement
While Fibonacci retracement levels are widely used, they are not without limitations. Here are some potential drawbacks:
- Subjectivity: The choice of high and low points for drawing Fibonacci retracement levels can be subjective, leading to different interpretations by different traders.
- False Signals: Fibonacci retracement levels can produce false signals, especially in volatile or choppy markets. It's essential to use other technical indicators to confirm potential reversal points.
- Not a Standalone Tool: Fibonacci retracement should not be used in isolation. It is most effective when combined with other technical analysis tools, such as trend lines, moving averages, and volume analysis.
Fibonacci Retracement Example and Analysis
Let's consider an example to understand how Fibonacci retracement levels can be applied in real trading scenarios.
Example: Trading an Uptrend
Suppose a stock has been in an uptrend, moving from a low of $50 to a high of $100. To draw the Fibonacci retracement levels, the trader would:
- Identify the low point at $50 and the high point at $100.
- Use the Fibonacci retracement tool to draw a line from $50 to $100.
- The tool generates the following retracement levels: 23.6% ($88.20), 38.2% ($80.90), 50% ($75.00), and 61.8% ($69.10).
As the price starts to retrace from $100, the trader watches for potential support at these levels. If the price retraces to the 38.2% level at $80.90 and starts to move higher, the trader might consider entering a long position, anticipating a continuation of the uptrend.
Fibonacci Retracement in Different Markets
Fibonacci retracement levels can be applied to various financial markets, including stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. The principles remain the same, but traders may need to adjust their approach based on the specific characteristics of each market.
1. Stocks
In the stock market, Fibonacci retracement levels are used to identify potential support and resistance levels during pullbacks in uptrends and downtrends. Traders often combine Fibonacci levels with other indicators like moving averages and volume analysis to increase the accuracy of their trades.
2. Forex
In the forex market, Fibonacci retracement levels are particularly useful due to the high volatility and frequent price swings. Forex traders use Fibonacci levels to find potential entry and exit points, as well as to set stop-loss and take-profit orders. Combining Fibonacci levels with other technical indicators, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), can help forex traders enhance their trading strategies.
3. Commodities
Commodity traders use Fibonacci retracement levels to identify potential price reversal points in markets such as gold, oil, and agricultural products. These levels can help traders make informed decisions about entering or exiting positions and managing risk effectively.
4. Cryptocurrencies
The cryptocurrency market is known for its high volatility and rapid price movements. Fibonacci retracement levels can be valuable tools for crypto traders, helping them identify potential support and resistance levels during market corrections. Given the nascent and highly speculative nature of cryptocurrencies, it is essential for traders to use Fibonacci levels in conjunction with other technical analysis tools to make well-informed decisions.
Combining Fibonacci Retracement with Other Technical Analysis Tools
To improve the reliability of Fibonacci retracement levels, traders often combine them with other technical analysis tools. Here are some commonly used combinations:
1. Trend Lines
Combining Fibonacci retracement levels with trend lines can provide additional confirmation of potential support and resistance levels. Trend lines help traders identify the overall direction of the market, and when they intersect with Fibonacci levels, it strengthens the likelihood of a reversal or continuation.
2. Moving Averages
Moving averages are widely used to smooth out price data and identify trends. When Fibonacci retracement levels align with moving averages, it enhances the significance of those levels. For example, if a Fibonacci retracement level coincides with a 50-day moving average, it becomes a stronger potential support or resistance level.
3. Volume Analysis
Volume analysis helps traders understand the strength and validity of price movements. When Fibonacci retracement levels coincide with high trading volume, it indicates stronger support or resistance. Traders can use volume spikes to confirm the significance of Fibonacci levels and make more informed trading decisions.
4. Oscillators
Oscillators such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) are used to identify overbought and oversold conditions in the market. When these indicators align with Fibonacci retracement levels, it provides additional confirmation for potential reversals or continuations. For example, if the RSI indicates an oversold condition at a 61.8% Fibonacci retracement level, it increases the likelihood of a bullish reversal.

Note - Fibonacci retracement is a powerful tool in technical analysis that helps traders identify potential support and resistance levels. By understanding the key Fibonacci ratios and how to apply them to different markets, traders can make more informed decisions and improve their trading strategies. However, it is important to remember that Fibonacci retracement levels should not be used in isolation. Combining them with other technical analysis tools and confirming signals can enhance their reliability and effectiveness. As with any trading strategy, proper risk management and continuous learning are essential for success in the financial markets.